



| Key Terms Every Fashion Student Should Know | |
|---|---|
| Term | Meaning |
| Avatar | A digital version of a person used in games or virtual spaces. |
| NFT (Non-Fungible Token) | A digital certificate proving ownership of a virtual item. |
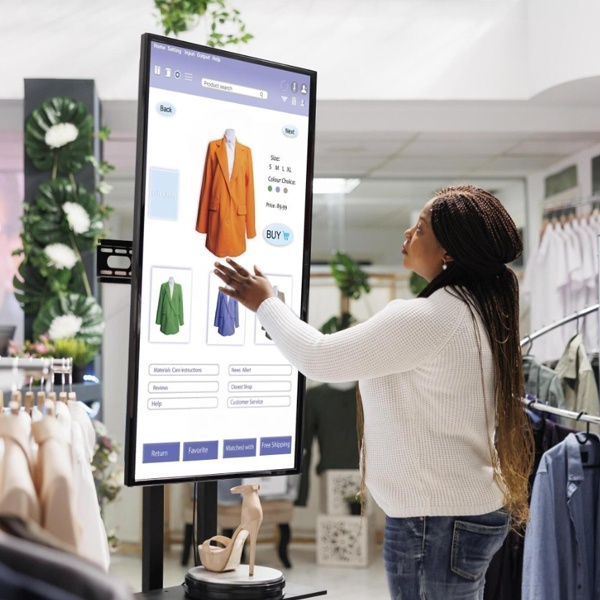
| AR (Augmented Reality) | Technology that overlays digital clothes on a real image. |
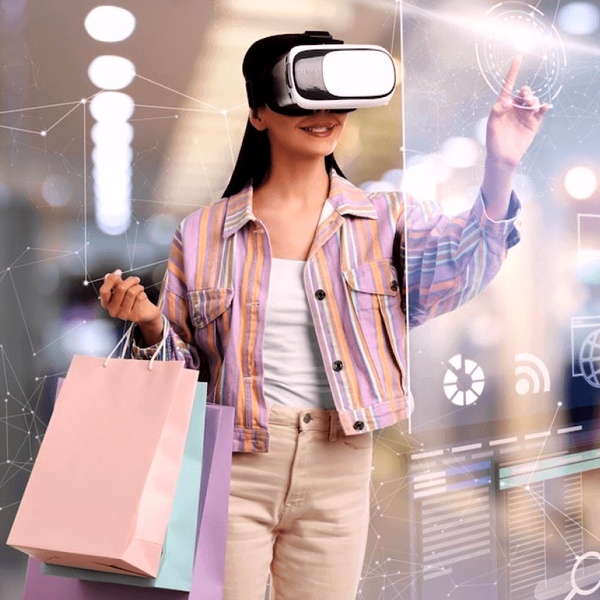
| VR (Virtual Reality) | A fully immersive 3D environment for digital fashion experiences. |
| Metaverse | A shared virtual world where users interact, shop and express style. |
| 3D Modelling | Creating a digital version of a garment in three dimensions. |
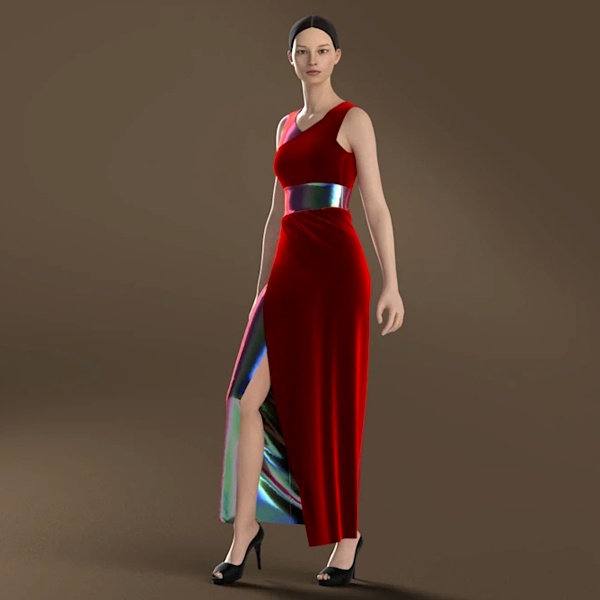
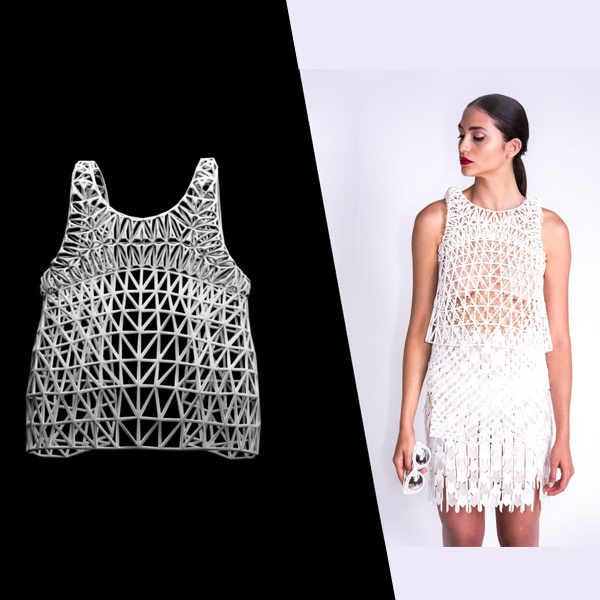












| Concept Development | Create mood boards and sketches to define the theme. |
| 3D Design Creation | Use 3D software to model garments, adjust textures and simulate fabric movement. |
| Virtual Fitting | Test your designs on digital avatars to refine fit and details. |
| Rendering & Presentation | Produce high-quality visuals or videos for portfolios, social media or online showcases. |
| Digital Publishing | Share your collection on platforms like DRESSX, The Fabricant or Instagram or use AR filters for interactive viewing. |
| Purpose | Recommended Tools / Platforms |
|---|---|
| 3D Design | CLO3D, Marvelous Designer, Blender |
| Rendering | KeyShot, Adobe Substance 3D |
| AR / VR Creation | Adobe Aero, Unity, Unreal Engine |
| Learning Platforms | Coursera, Udemy, Skillshare, FutureLearn |
| Design Communities | ArtStation, Behance, Discord fashion design groups |
Yes, you can. But remember - NFT's and digital assets are taxable under Indian law. You might need to pay GST or income tax on sales.
Learn tools like CLO3D, Marvelous Designer, Blender and Photoshop. A basic grasp of textures, 3D modelling and virtual styling will help you stand out.
Yes. Many design institutes and private academies now teach 3D fashion and CLO3D. Always check if they offer hands-on projects and updated software before joining.
You can work as a 3D garment artist, digital stylist, AR/VR fashion designer or virtual merchandiser. Some Indian brands already hire designers for digital try-ons and metaverse launches.
Yes, quite a few are exploring it - especially luxury and D2C labels. Virtual try-ons, digital runways and 3D product previews are slowly becoming part of marketing and e-commerce.
Yes, you can sell on global platforms like DressX, Drest or metaverse stores. Payments should come through proper banking channels as per RBI rules.
Keep original files private, watermark your work and use contracts when sharing with clients. You can also mint NFT's for proof of ownership, though that doesn't replace legal IP rights.
It helps reduce fabric waste and overproduction, especially during sampling. But remember - rendering and blockchain processes also use energy. The impact depends on how consciously it is used.
You can start by creating virtual outfits for social media, stylists, influencers or by collaborating with brands for digital lookbooks. You don't need to build your own tech setup at first.
Absolutely, but do it respectfully. Keep the cultural details right and, if possible, collaborate with artisans whose designs inspire your work.
Probably not. It's more about blending - real fashion for daily life, digital fashion for online presence, gaming and social media.
AI helps in predicting trends, creating realistic avatars and automating fabric simulations. It is changing how designers imagine and test new collections.
Yes! Many people come from gaming, animation or computer backgrounds. As long as you are creative and willing to learn design basics, you can grow here.
It is just beginning - but growing fast. With more virtual influencers, metaverse events and sustainable fashion goals, digital design will soon become a regular part of the fashion world.
 CONTACT USWaves Institute of Fashion Designing,
CONTACT USWaves Institute of Fashion Designing,